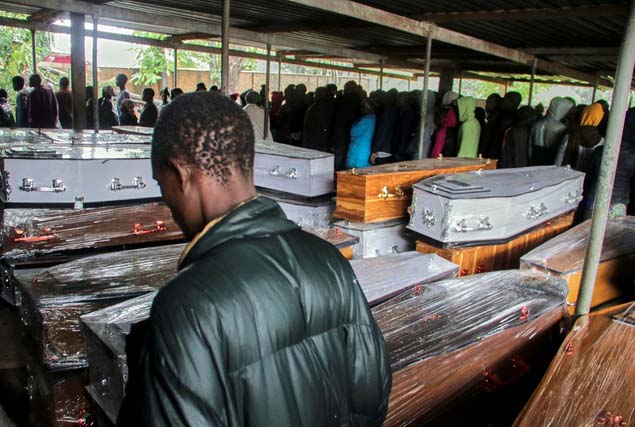
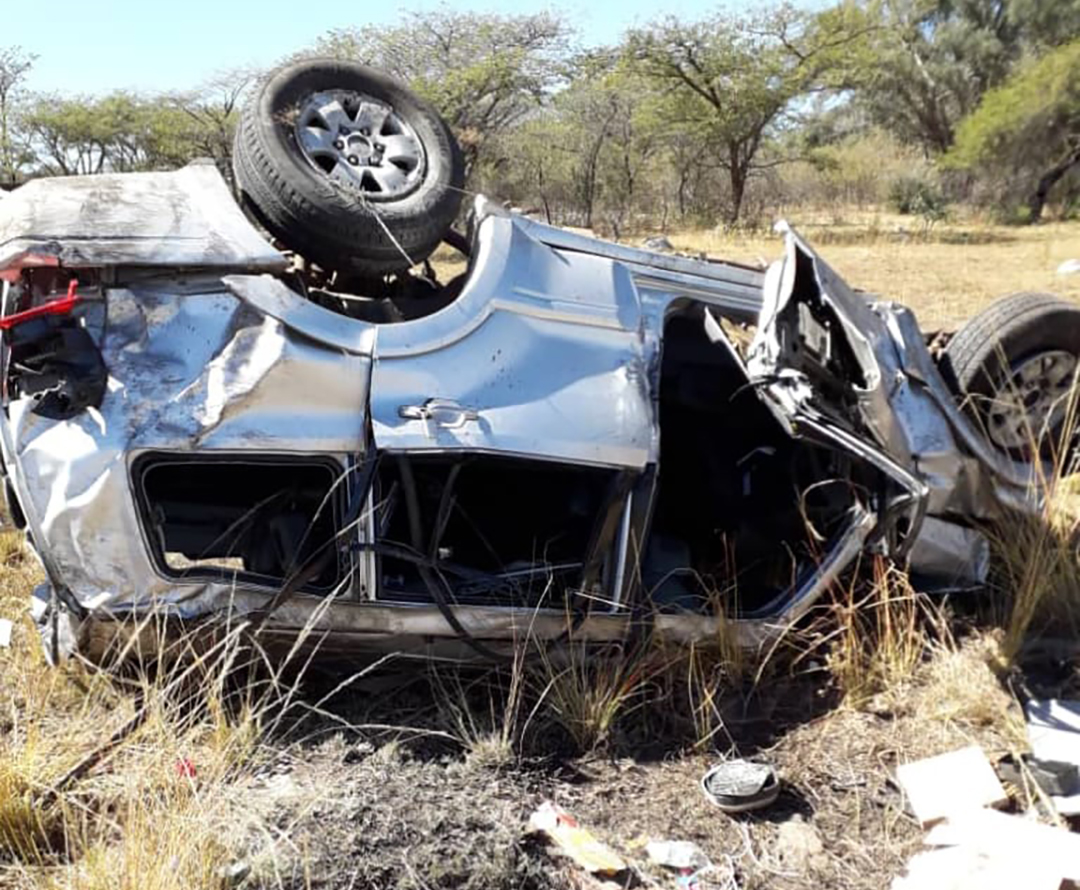
JOHANNESBURG, South Africa – Tropical cyclone Freddy hit the coast of southern Africa for a second time over the weekend, bringing its total death toll to more than 220 people in Malawi, Mozambique and Madagascar.
The month-long storm has broken at least one record and could break two more, meteorologists say.
As climate change causes warmer oceans, heat energy from the water’s surface is fuelling stronger storms.
Below are some of the main reasons Freddy is noteworthy.
Freddy holds the record for most accumulated cyclone energy (ACE), a measure based on a storm’s wind strength over its lifetime, of any storm in the southern hemisphere and possibly worldwide.
Freddy has generated about as much accumulated cyclone energy as an average full North Atlantic hurricane season, according to the World Meteorological Organisation.
By last week it was in second place for the most accumulated cyclone energy of any storm since 1980, with the record held by Hurricane and Typhoon Ioke in 2006.
Some estimates show that Freddy has since broken that record, with 86 ACE compared to Ioke’s 85 ACE.
Freddy may have broken the record for longest-lasting tropical cyclone on record, according to the World Meteorological Organisation.
The current record is held by a 31-day hurricane in 1994.
Freddy first developed on February 6 and made its second landfall on the coast of Mozambique on March 11 – 34 days later.
However, experts still have to look at several factors, such as the fact that it weakened below tropical cyclone status at some points during that time, in order to determine whether it broke the record, the World Meteorological Organisation said.
Freddy appears to have broken the world record for the most bouts of rapid intensification, defined as an increase in wind speed of 56km per hour in a period of 24 hours.
Freddy had seven separate cycles of rapid intensification, according to satellite estimates, said the World Meteorological Organisation. The previous record was four, which was reached by several hurricanes.
The World Meteorological Organisation will set up an expert committee to examine this record, as well as the others, it said.
Freddy developed off the coast of Australia, crossed the entire South Indian Ocean and travelled more than 8,000km to make landfall in Madagascar and Mozambique in late February.
It then looped back and hit the coast of Mozambique again two weeks later, before moving inland to Malawi.
“No other tropical cyclones observed in this part of the world have taken such a path across the Indian Ocean in the past two decades,” said the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in an article.
Only four storms have crossed the southern Indian Ocean from east to west, with the last one in 2000, it said. – Reuters